Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Kernel KMeans clustering with GEMINI¶
Since the MMD GEMINI objective is equivalent in OvO mode to a kernel KMeans objective, we can use it with the nonparametric model that directly associates a cluster to each sample. The overall model would thus behave as a kernel KMeans algorithm. However, its training is done by gradient descent.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn import metrics, datasets
from gemclus.nonparametric import CategoricalMMD
Draw samples from a circular dataset¶
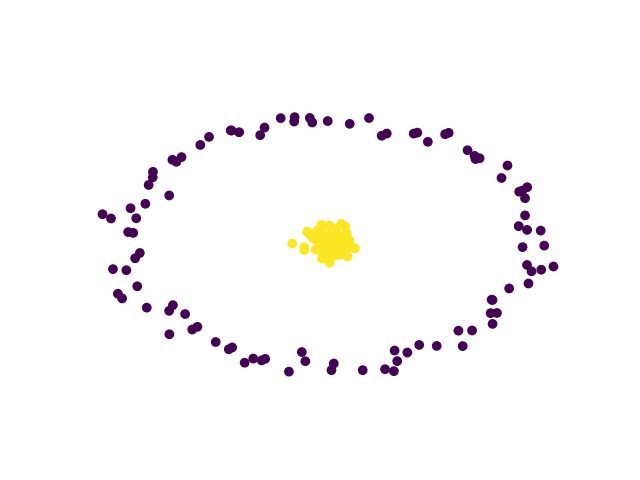
# We start by generating samples distributed on two circles
X, y = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=200, noise=0.05, factor=0.05, random_state=0)
# then normalise the data
X = (X - np.mean(X, 0)) / np.std(X, ddof=0)
# Have a look at it
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y)
plt.axis("off")
plt.ylim((-3, 3))
plt.ylim((-3, 3))
plt.show()
Train the model¶
Create the Non parametric GEMINI clustering model and call the .fit method to optimise the cluster assignment of the nodes
model = CategoricalMMD(n_clusters=2, random_state=0, kernel="rbf")
y_pred = model.fit_predict(X)
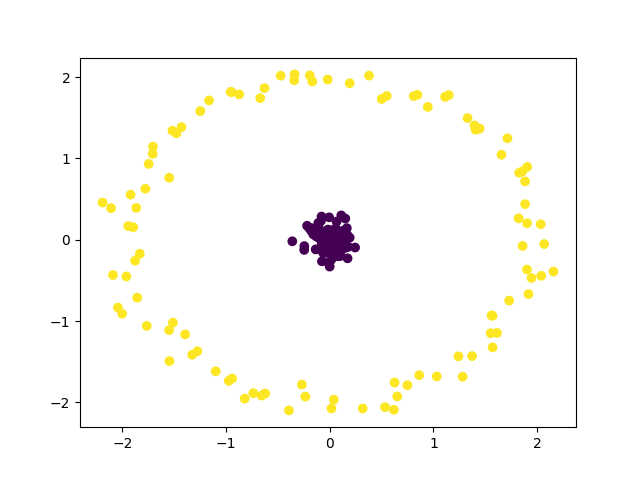
Final Clustering¶
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y_pred)
plt.show()
ari_score = metrics.adjusted_rand_score(y, y_pred)
gemini_score = model.score(X)
print(f"Final ARI score: {ari_score:.3f}")
print(f"GEMINI score is {gemini_score:.3f}")
Final ARI score: 1.000
GEMINI score is 0.330
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.707 seconds)