Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
An introducing example to clustering with an MLP and the MMD GEMINI¶
We show in this example how to use the gemclus.mlp.MLPMMD to fit a simple mixture of Gaussian distributions. The architecture here is a two-layer neural network trained with the MMD GEMINI, an objective equivalent to kernel KMeans.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from gemclus.mlp import MLPMMD
Generate data¶
X, y = datasets.make_blobs(centers=3, cluster_std=0.5, n_samples=200, random_state=0)
Create the MLP clustering model and fit it¶
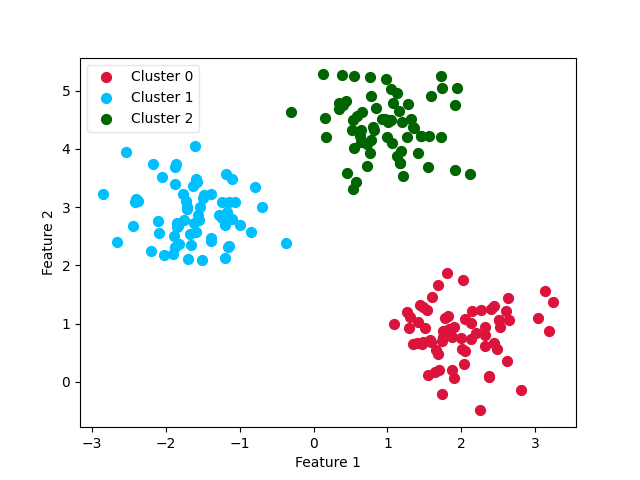
Plot the final clustering¶
y_pred = clf.predict(X)
X_0 = X[y_pred == 0]
X_1 = X[y_pred == 1]
X_2 = X[y_pred == 2]
ax0 = plt.scatter(X_0[:, 0], X_0[:, 1], c='crimson', s=50)
ax1 = plt.scatter(X_1[:, 0], X_1[:, 1], c='deepskyblue', s=50)
ax2 = plt.scatter(X_2[:, 0], X_2[:, 1], c='darkgreen', s=50)
leg = plt.legend([ax0, ax1, ax2],
['Cluster 0', 'Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2'],
loc='upper left', fancybox=True, scatterpoints=1)
leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5)
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.ylabel('Feature 2')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.686 seconds)