Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Comparative clustering of circles dataset with kernel change¶
We show here a simple dataset consisting in two centred circle that can be challenging for some clustering algorithms. This dataset can be challenging for GEMINI as well, unless we change the kernel adequately.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import metrics
from gemclus.linear import KernelRIM
Draw samples for the circle dataset¶
Training clustering model¶
model_kernel = KernelRIM(n_clusters=2, base_kernel="laplacian", max_iter=1000, reg=4/len(X), random_state=0)
y_pred = model_kernel.fit_predict(X)
print(f"ARI = {metrics.adjusted_rand_score(y, y_pred)}")
ARI = 1.0
Show predictions on similar samples¶
# Create a novel set of samples and cluster them
new_X, new_y = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=200, noise=noise, factor=factor, random_state=1)
new_pred = model_kernel.predict(new_X)
print(f"ARI = {metrics.adjusted_rand_score(new_y, new_pred)}")
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y_pred, marker="+", label="Training samples")
plt.scatter(new_X[:, 0], new_X[:, 1], c=new_pred, marker="o", label="Testing samples")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
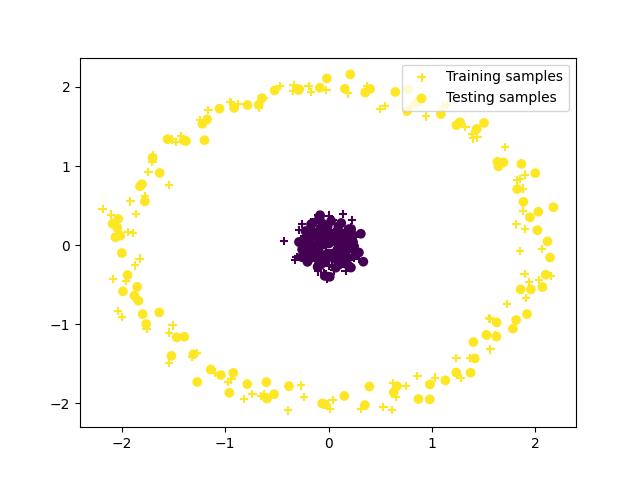
ARI = 1.0
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.959 seconds)